How are Viruses different from Bacteria apex? You’ve come to the right place! In this article, you will comprehend the distinct characteristics that make bacteria and viruses distinctive. We’ll examine their dimensions, their structure, how they reproduce, and their life cycle, diving into the fascinating world of tiny organisms. Let’s examine How are Viruses different from Bacteria apex?
In the world of microscopic organisms, viruses as well as bacteria apex are fascinating and vital elements of life. Despite their small dimensions, they are essential to the functioning of ecosystems, and they can have an impact on the health of humans. In this article, we’ll examine the distinctive characteristics that distinguish bacteria and viruses apart from one another. When we understand their differences it will be possible to learn more about their role’s impact, as well as consequences for our environment.
How are Viruses different from Bacteria apex?
The heart of our discussion is the most fundamental question: How are Viruses different from Bacteria apex? Let’s examine this question deeply to find out the distinct characteristics that define the two different types of microorganisms.
Structure and Composition
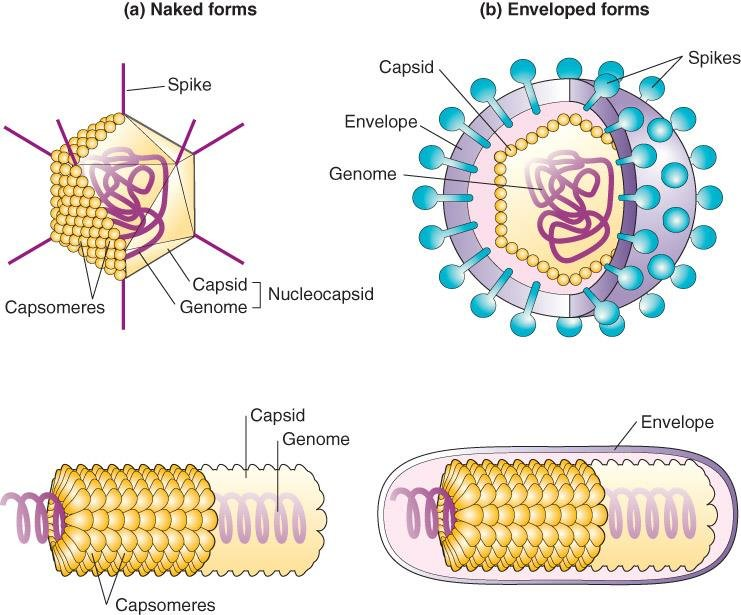
Viruses: Viruses are smaller and have a simpler structure than bacteria’s apex. They comprise genetic material, such as DNA or RNA, that is encased within a protein coat known as the capsid. Some viruses also have an outer lipid shell that is derived from the membrane of the host cell.
Bacteria Apex: Bacteria Apex is, however, single-celled organisms that have more intricate structures. They contain a cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material that is DNA that is located in the nucleoid area.
Size
Viral particles are extremely small when compared to bacteria cells. They usually range somewhere between 200 and 300 nanometers in size.
Bacteria grow larger, generally being between 0.5 to five micrometers (m)
Biological Classification
Viruses: Viruses aren’t considered living organisms due to their lack of the structure of cells and metabolic processes typical of living cells. They are essentially DNA or RNA (DNA, also known as RNA) enclosed in a protein cover.
Bacteria; Bacteria are single-celled prokaryotic organisms. They are considered living beings because they contain identifiable nuclei and can perform a variety of metabolic tasks.
Reproduction Mechanism
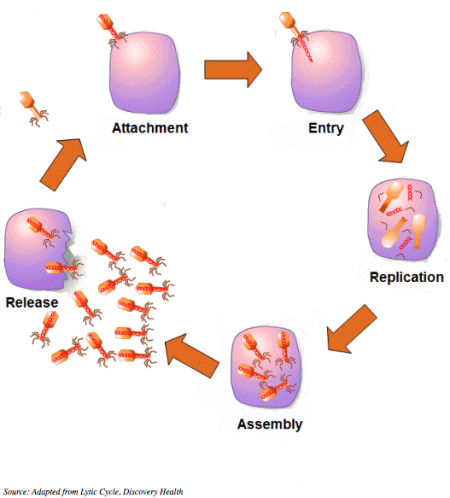
Viruses: Viruses can’t reproduce by themselves. They depend on infecting host cells to reproduce and generate new viruses. Viruses inject their DNA into the host cell, stealing the machinery of cells to replicate their components and create new viruses.
Bacteria Apex: Bacteria apex reproduces via the process of binary fission. Through this process, the bacterial cell divides into identical twin cells. The rapid reproduction process contributes to the expansion of bacterial populations.
Life Cycle
Viruses: The virus must borrow the host cell’s resources to create copies of itself. Once inside the host cell, it becomes part of the cell’s machinery to reproduce its genes and produce additional virus particles. Unfortunately, this usually results in the death of the host cell and a rash of disease-related symptoms.
Bacteria: On the other hand, have a more intricate life cycle. They reproduce by splitting into two identical cells in the process of binary fission. In addition, bacteria are able to use their genetic material to share through conjugation, which can help them develop new characteristics and adapt to different conditions.
Cellular Complexity
Viruses: Viruses lack cellular complexity. They are regarded as intracellular parasites since they require an organelle to carry out their reproductive process.
Bacteria Apex: Bacteria Apex are complete single-celled creatures with complex cellular structures. They are capable of carrying out crucial life-sustaining processes on their own.
Living or Nonliving
Viruses: The classification of viruses as non-living or living is a topic of controversy. Although they have characteristics similar to those of living organisms, like genetic material, viruses lack other characteristics, like the capacity to carry out metabolic processes.
Bacteria Apex: Bacteria are unquestionably living organisms. They are able to metabolize, expand, and adapt to their surroundings.
Antibiotic Sensitivity
Viruses: Viruses are not affected by antibiotics because they are primarily aimed at the cellular processes that viruses lack.
Bacteria Apex: The Bacteria apex may be irritable to antibiotics which hinders their reproduction and growth.
Impact on Human Health
Viruses: Viruses can trigger various illnesses in humans, such as the common cold as well as flu, HIV as well as COVID-19. Vaccines are commonly employed to stop viral diseases.
Bacteria Apex: Bacteria Apex causes many diseases, such as tuberculosis, strep throat, and urinary tract infections. Antibiotics are often employed to combat bacterial infections.
Mode of Infection
Do you know how viruses and bacteria can enter your body, causing infections? It’s essential to know how to differentiate them. Let’s take it apart:
- Host Specificity: Bacteria and viruses have their distinct characteristics when they infect living organisms. Viruses are very specific and typically have a limited range of hosts.
For example, a specific virus may only infect humans or a certain kind of animal. Conversely, bacteria possess an extensive host range. They are able to infect animals, humans, or even plants and thrive in different settings.
- Entry Mechanisms: The method by which bacteria and viruses get into the body is very different. Viruses usually enter the body by adhering to receptors that are specific to their host cell. These receptors work as locks, and the virus is carrying its key (in its form in gene material) to open and be able to enter the cell.
Once in the host cell, the virus will take over the host cell’s machinery to multiply itself. Bacteria, on the contrary, have many entry points. They can enter your body through breathing, as you inhale airborne bacteria, or via consumption of drinking water or food. In addition, wounds can be the entryway for bacteria.
- Immune Response: When the body is aware of a bacterium or virus and the immune system is activated, it springs into Response. However, the Response to infection differs between the two kinds of pathogens. Viruses can be difficult to combat because they can defy immune detection and even manipulate host cells to reproduce.
This makes it difficult for your body’s immune system to identify and eliminate them efficiently. Bacteria, however, frequently produce toxins as part of their strategy to fight infection. They can harm our body’s tissues directly and impact the immune system.
Metabolism

Viruses: Viruses lack metabolism mechanisms. They aren’t able to perform cell-based processes such as respiration, growth, or any other.
Bacteria: Bacteria perform metabolic functions and can produce energy using various mechanisms, including respiration, photosynthesis, and fermentation.
FAQs: How are Viruses different from Bacteria apex?
How are Viruses different from Bacteria apex?
A virus isn’t an organism living and can only reproduce and grow in its host cells. Bacteria are single-celled organisms that generate the energy they require and reproduce independently. While both can cause disease, bacteria also play important and beneficial functions in the natural world.
How are bacteria different from viruses apex?
Bacteria are single cells that are able to exist on their own either inside or outside of the body. Infections are caused by viruses infiltrating and multiplying within the host’s cells. It can be challenging to pinpoint the cause of an infection since bacteria and viral infections can result in similar symptoms.
How Does Infection Work?
Infection can occur when bacteria, viruses, or other microbes invade your system and then begin to increase in number. There is a strong connection between microbes and human beings. Experts believe that around 50% of human DNA was created by viruses that infected, and then embedded their nucleic acid into the egg of our ancestors and Sperm cells.
Can antibiotics be effective against both viral and bacterial infections?
Bacteria cause bacterial infections. Viral infections are caused by viruses. Antibiotic medications kill or stop some bacteria from forming but don’t treat viruses. Antiviral medications help your body eliminate certain viruses.
What are the ways that bacteria can have an impact on the human body’s health?
The bacteria that live in our bodies aid in degrading the food we eat, and help provide nutrients to us and neutralize the effects of toxins. They play a crucial function in defending against infections, by defending healthy surfaces from invaders.